
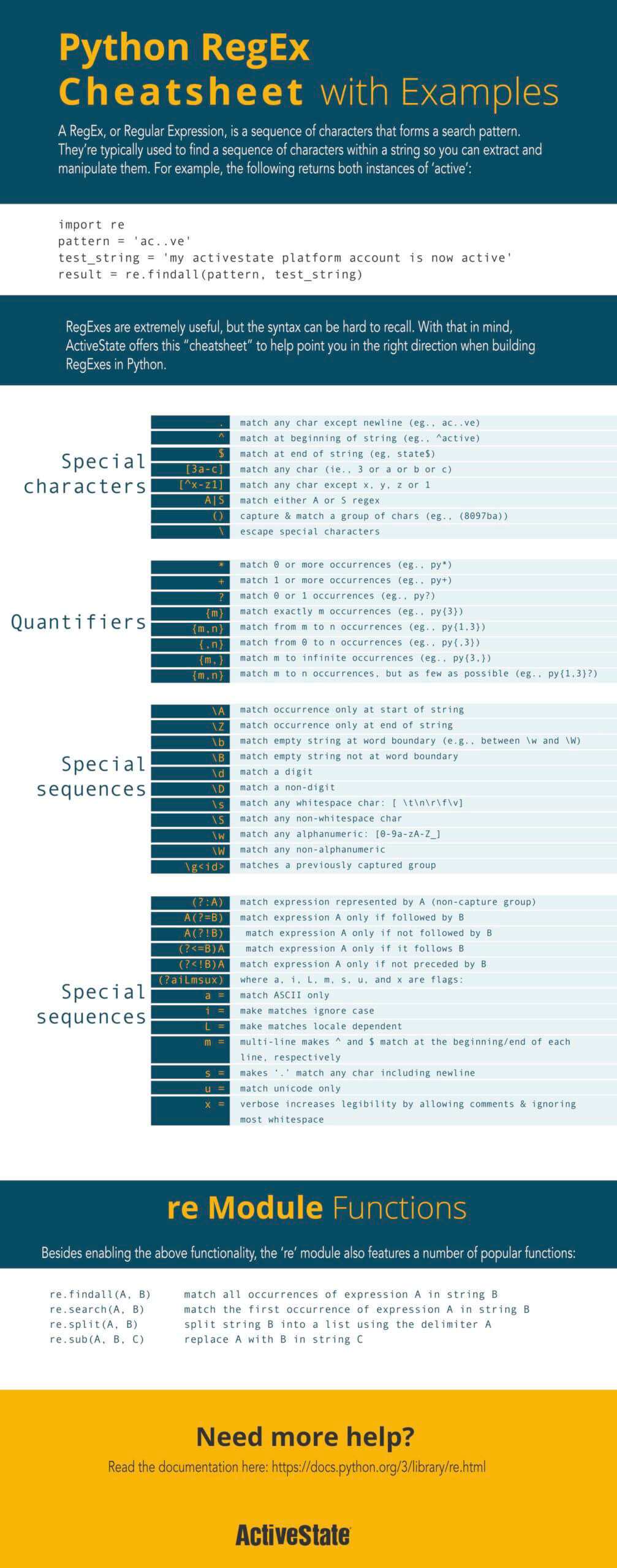
Individual Sheet Descriptions. Beginner’s Python Cheat Sheet Provides an overview of the basics of Python including variables, lists, dictionaries, functions, classes, and more. Beginner’s Python Cheat Sheet - Lists Focuses on lists: how to build and modify a list, access elements from a list, and loop through the values in a list.
Basics
| Print a number | print(123) |
| Print a string | print('test') |
| Adding numbers | print(1+2) |
| Variable assignment | number = 123 |
| Print a variable | print(number) |
| Function call | x = min(1, 2) |
| Comment | # a comment |
Types
| Integer | 42 |
| String | 'a string' |
| List | [1, 2, 3] |
| Tuple | (1, 2, 3) |
| Boolean | True |
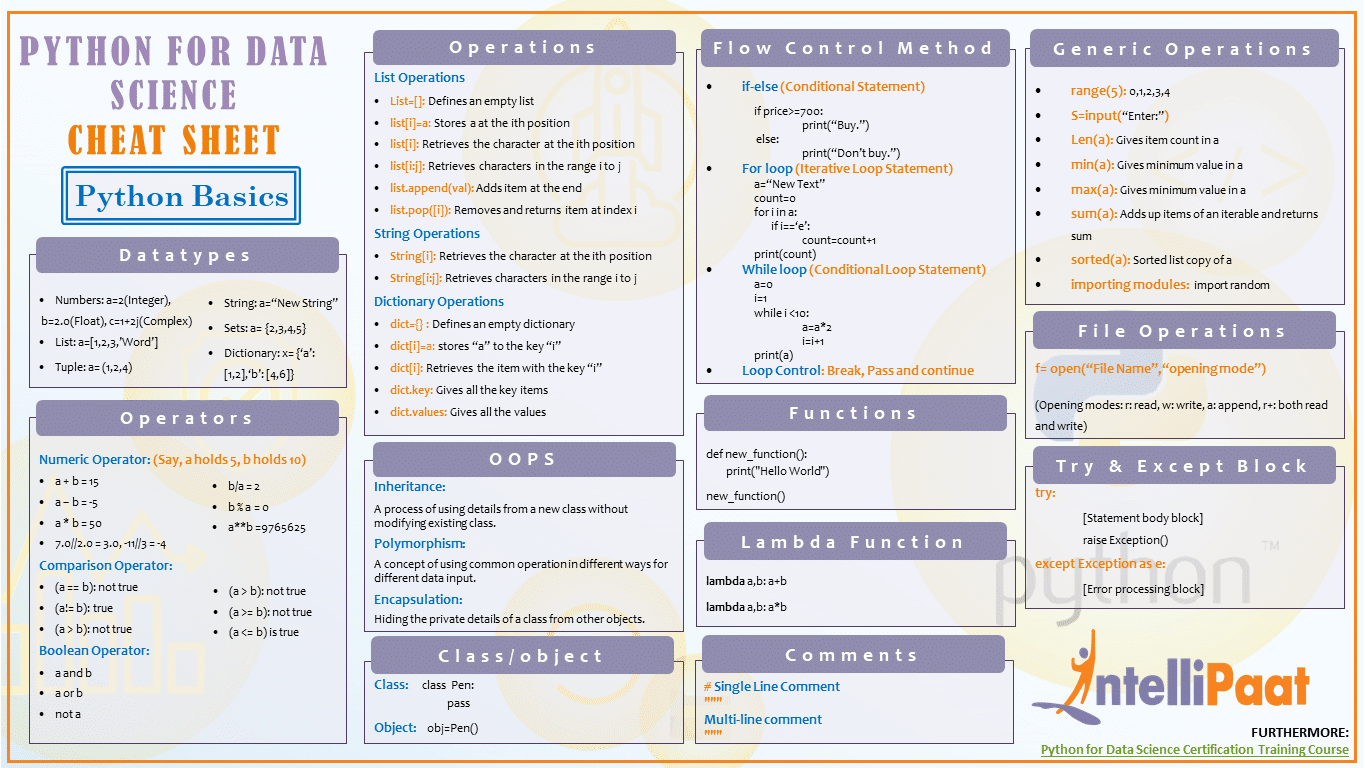
- Python’s list comprehension is a very useful asset for a programmer and a reason for us to love Python. It’s a special syntax, creating lists out of lists and transforming many lines of code into a single one.
- Python is a beautiful language. It's easy to learn and fun, and its syntax is simple yet elegant. Python is a popular choice for beginners, yet still powerful enough to to back some of the world’s most popular products and applications from companies like NASA, Google, Mozilla, Cisco, Microsoft, and Instagram, among others.
- Beginner’s Python Cheat Sheet - Dictionaries Focuses on dictionaries: how to build and modify a dictionary, access the information in a dictionary, and loop through dictionaries in a variety of ways. Includes sections on nesting lists and dictionaries, using dictionary comprehensions, and more.
- So download a copy of our Python cheat sheet and get that first.py program up and running! PDF Version of Python Cheat Sheet. Python Cheat Sheet (Download PDF) Infographic Version of Python Cheat Sheet (PNG) Python Cheat Sheet (Download PNG) Python Cheat Sheet Python Basics: Getting Started. Most Windows and Mac computers come with Python pre.
Useful functions
| Write to the screen | print('hi') |
| Calculate length | len('test') |
| Minimum of numbers | min(1, 2) |
| Maximum of numbers | max(1, 2) |
| Cast to integer | int('123') |
| Cast to string | str(123) |
| Cast to boolean | bool(1) |
| Range of numbers | range(5, 10) |
Other syntax
| Return a value | return 123 |
| Indexing | 'test'[0] |
| Slicing | 'test'[1:3] |
| Continue to next loop iteration | continue |
| Exit the loop | break |
| List append | numbers = numbers + [4] |
| List append (with method call) | numbers.append(4) |
| List item extraction | value = numbers[0] |
| List item assignment | numbers[0] = 123 |
Terminology
| syntax | the arrangement of letters and symbols in code |
| program | a series of instructions for the computer |
| print | write text to the screen |
| string | a sequence of letters surrounded by quotes |
| variable | a storage space for values |
| value | examples: a string, an integer, a boolean |
| assignment | using = to put a value into a variable |
| function | a machine you put values into and values come out |
| call (a function) | to run the code of the function |
| argument | the input to a function call |
| parameter | the input to a function definition |
| return value | the value that is sent out of a function |
| conditional | an instruction that's only run if a condition holds |
| loop | a way to repeatedly run instructions |
| list | a type of value that holds other values |
| tuple | like a list, but cannot be changed |
| indexing | extracting one element at a certain position |
| slicing | extracting some elements in a row |
| dictionary | a mapping from keys to values |
Reminders
- Strings and lists are indexed starting at 0, not 1
- Print and return are not the same concept
- The return keyword is only valid inside functions
- Strings must be surrounded by quotes
- You cannot put spaces in variable or function names
- You cannot add strings and integers without casting
- Consistent indentation matters
- Use a colon when writing conditionals, function definitions, and loops
- Descriptive variable names help you understand your code better
Conditionals
Lists
Python Basic Syntax Sheet Pdf

Basic Python Syntax Cheat Sheet Pdf
Defining functions
Loops
Dictionaries
Comparisons
| Equals |
| Not equals | != |
| Less than | < |
| Less than or equal | <= |
| Greater than | > |
Useful methods
| String to lowercase | 'xx'.lower() |
| String to uppercase | 'xx'.upper() |
| Split string by spaces | 'a b c'.split(' ') |
| Remove whitespace around string | ' a string '.strip() |
| Combine strings into one string | ' '.join(['a', 'b']) |
| String starts with | 'xx'.startswith('x') |
| String ends with | 'xx'.endswith('x') |
| List count | [1, 2].count(2) |
| List remove | [1, 2].remove(2) |
| Dictionary keys | {1: 2}.keys() |
| Dictionary values | {1: 2}.values() |
| Dictionary key/value pairs | {1: 2}.items() |
Other neat bonus stuff
Python Basic Syntax Pdf
| Zip lists | zip([1, 2], ['one', 'two']) |
| Set | my_set = {1, 2, 3} |
| Set intersection | {1, 2} & {2, 3} |
| Set union | {1, 2} | {2, 3} |
| Index of list element | [1, 2, 3].index(2) |
| Sort a list | numbers.sort() |
| Reverse a list | numbers.reverse() |
| Sum of list | sum([1, 2, 3]) |
| Numbering of list elements | for i, item in enumerate(items): |
| Read a file line by line | for line in open('file.txt'): |
| Read file contents | contents = open('file.txt').read() |
| Random number between 1 and 10 | import random; x = random.randint(1, 10) |
| List comprehensions | [x+1 for x in numbers] |
| Check if any condition holds | any([True, False]) |
| Check if all conditions hold | all([True, False]) |
Python Syntax Cheat Sheet Pdf
Missing something?
Let us know here.








